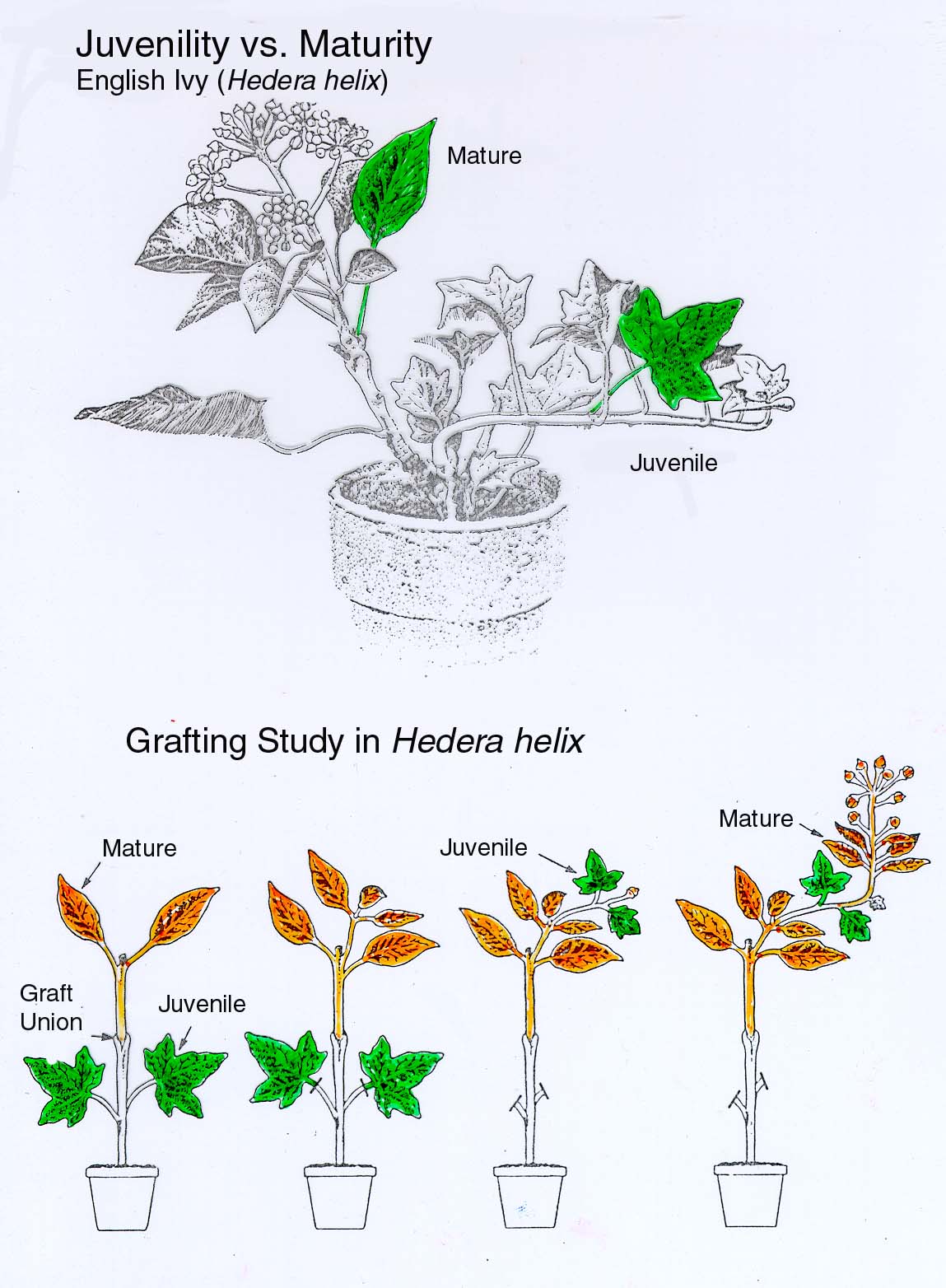
- Function
- Bioassay
- Site of Synthesis
 Chemistry
Chemistry
-Promote cell growth and elongation, alters cell wall plasticity
-Responsible for apical dominance and phototropism
-Promote calusing and rooting
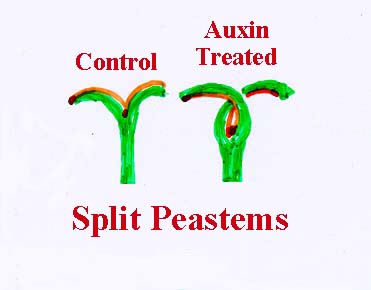
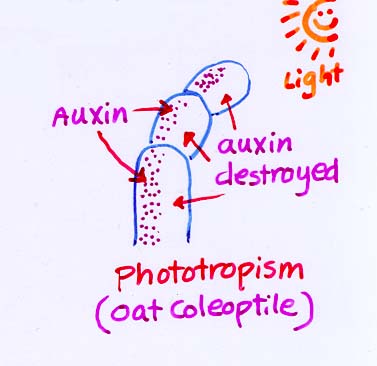 -Directing movement (shoot apex----downward)
-Directing movement (shoot apex----downward)
-Split pea stem curvature study
-Oat coleoptile test for photoropism
-Stem apex (growing point)
-Present abundantly in actively growing shoot tips
IAA- Indoleacetic Acid (Natural)
NAA- Naphthaleneacetic Acid (synthetic)
IBA- Indolebutyric Acid (synthetic)
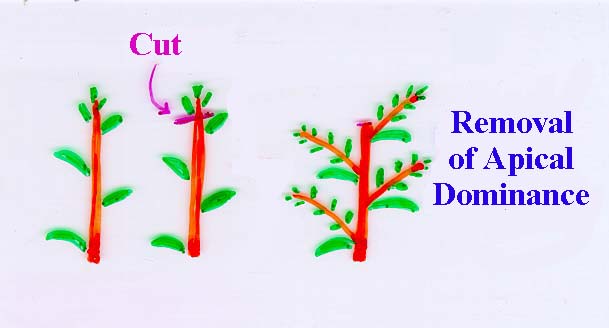

 -Regulates synthesis of DNA, RNA, Protein
-Regulates synthesis of DNA, RNA, Protein Chemistry
Chemistry Muskemlon: Andromonoecious (male, female)----Eth-à
gynomonoecious (male/female)
Muskemlon: Andromonoecious (male, female)----Eth-à
gynomonoecious (male/female)