I. Introduction
1. Functios
of Soil
- Plant anchorage
- Provides water to plants
- Supplies mineral nutrients to plants
2.
Four Components of Soil
-
mineral
- organic matter
- water
- air
3. The Functional Phases of Soil
a.
Solid phase - soil particles (clay,
sand, silt, etc.)
b. Gas
phase - provides oxygen
c. Liquid phase - supplies water
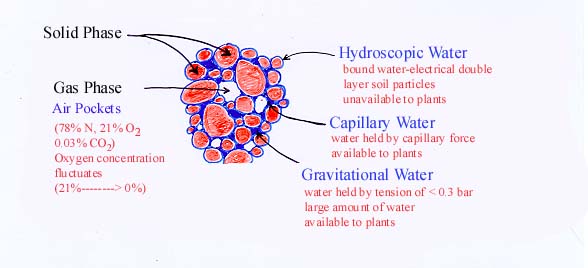
Field Capacity - the soil moisture condition obtained when all gravitational water is drained from the soil after field saturation4. Soil TextureContainer Capacity - same as field capacity for potted soil used in greenhouse
- Varies by presence of sand, silt, clay, loam
Heavy soil - high in clay and other fine particles
Light soil - low in clay and high in sand
and coarse particles
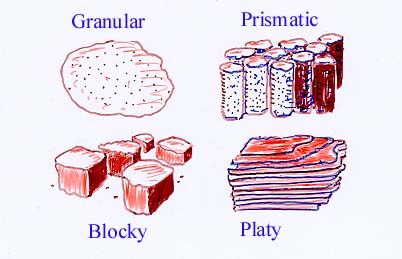
5. Soil Structure
- Arrangement of soil particles into aggregates formed by flocculation and granulation
6. Exchange Capacity
a.
Cation Exchange Capacity
(CEC)
- The ability of soil particles to absorb and store cations (measured in meq/100g soil)
II. Soil Reaction (pH)Cation = positively charged ion (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, NH4+)
b. Anion Exchange Capacity (AEC)Clay and organic particles have high CEC.
- The ability of soil particles to absorb (adsorb) and store anions (measured in meq/100g soil)
Anion = negatively charged ion (NO3-, SO42-, Cl-)
Most soils have little or no AEC

Strength of cation replacement
H+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Mg2+ > K+ > Na+
pH = - log [H+]
IV. Synthetic Soils (Artificial Mixes)1. Definition - soil acidity or alkalinity expressed in pH
2. Why is optimum soil pH important?
a. Nutrient availability
3. The soil pH optimumDeficiency, toxicity can be avoided
- Fe deficiency at high soil pH
- Al toxicity at low soil pHb. Microorganism activity
Needed for decomposition of organic matter (OM)
c. Nitrogen fixation and nitrification
Ammonifying nitrifying bacteria
Actinomycetes Nitrosomonas Nitrobacters
OM ------------------------ NH4+ ---------------------- NO2- ------------------- NO3-
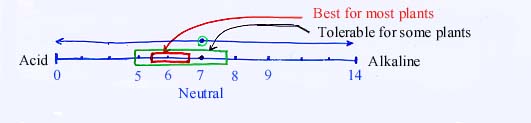
a. Most plants prefer 5.5 -7.0
4. Adjustment of Soil pHb. Acid loving plants
Blueberry - prefers a pH range from 4.0 to 5.5
c. Alkalinity tolerant plants
Azalea - prefers a pH range from 4.5 to 5.5Hydrangea
- Flower color turns blue at pH 4.5 - 5.5
- Flower color turns pink at pH 6.5 - 7.5
Asparagus - prefers a pH range of 6.5 to 7.9
Alfalfa - prefers a pH range of 6.5 to 7.7
Sugarbeet - prefers a pH range of 6.5 to 7.7
a. To raise soil pH, use:
- ground limestone
- dolomitic lime (mix of CaCO3 + MgCO3)
- gypsum (CaSO4)b. To lower soil pH, use:
- sulfur powder (S)
- aluminum sulfate (Al2 (SO4)3)- iron sulfate (FeSO4) Also for solutions, use:
- sulfuric acid (H2SO4 -----> 2H+ + SO4-2)
- phosphoric acid (H3PO4 -----> 3H+ + PO4-3)
- nitric acid (HNO3 -----> H+ + NO3-)
Sand - low water-holding, low CEC, heavy,
size varies
inert medium
Vermiculite - expanded mica mineral
high H2O
holding, good CEC, high buffering
Perlite - heated, popped volcanic rock, inert
very light, no CEC, no buffering, no nutrient holding
Calcined clay- Baked montmorillonite clay
aggregate particles, heavy, durable high
CEC
Pumice - crushed volcanic rock, inert
low waterholding, low CEC
b. Organic components
Crop residues -Straw, peanut hull, dry foliage, etc.Peatmoss - 75% decomposed
low in pH, high in CEC, high waterholding
high in C, add N when decomposting
Bark or sawdust - redwood, pine, fir, etc.
phenolic compounds phytotoxic, wait until
decomposted
2. Mixes Containing Soil4. Commercial Soil Mixes (used for nursery crops)a. For heavy soils, use:
1 part clay loam
2 parts organic matter
2 parts coarse aggregateb. For medium-textured soil,s use:
1 part silty loam
1 part organic matter
1 part coarse aggregatec. For light soils, use:
1 part sandy loam
1 part organic matterFor all mixes, use base fertilizers:Limestone - 6 to 8 oz/bushel
Superphosphate - 8 to 10 oz/bushel
a. UC-Mixes
| UC Mix | Percent sand | Percent peat |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b. Cornell Mix (Soilless Mix)Mix APeat-lite mix
- Extensively used for greenhouse crops
- Most commercial mixes are based on Cornell Mix formula
(e.g., Sunshine Mix, Pro-Mix)
Mix B1 part peat (sphagnum)
1 part vermiculite
plus base fertilizers
- ground limestone
- super phosphate
- calcium nitrate
- calcium nitrate
- trace elements, and
- wetting agent
1 Part sphagnum peatMix C
1 Part perlite
plus base fertilizers2 parts peat (sphagnum)
1 part vermiculite
1 part perlite
Plus base fertilizers