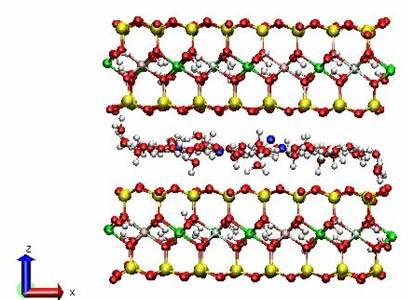
| Clay Water Interactions in Swelling Clays
|
|||||||
|
Back to research pages of:
TV Interviews
June 2005
Fall 2002
|
|
(Nelson and Miller, 1992)
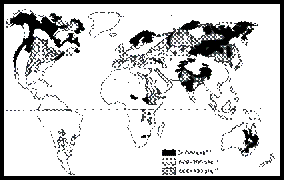
Extent of Swelling Clay Deposits in the United States
(Bordchardt, 1989) Swelling Clay Deposits Around the World Applications:
Katti, D.R., and Shanmugasundaram, V., (2001), Effect of Controlled Swelling on the Microstructure of Saturated Expansive Soil, Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 38, pp 175-182.
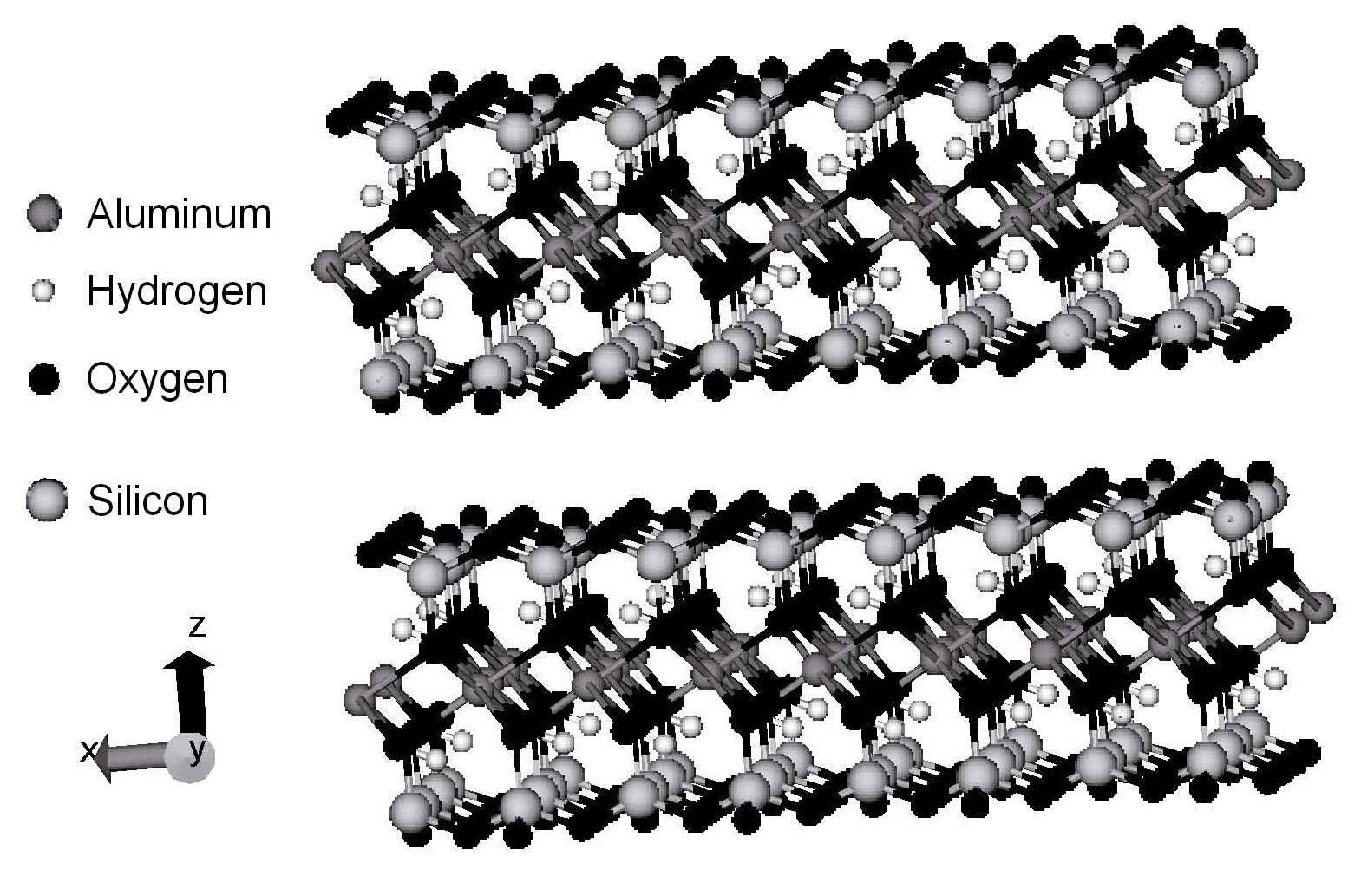
Steered Molecular Dynamics Modeling and Simulation of Pyrophyllite Clay Interlayer to Evaluate Mechanical Response
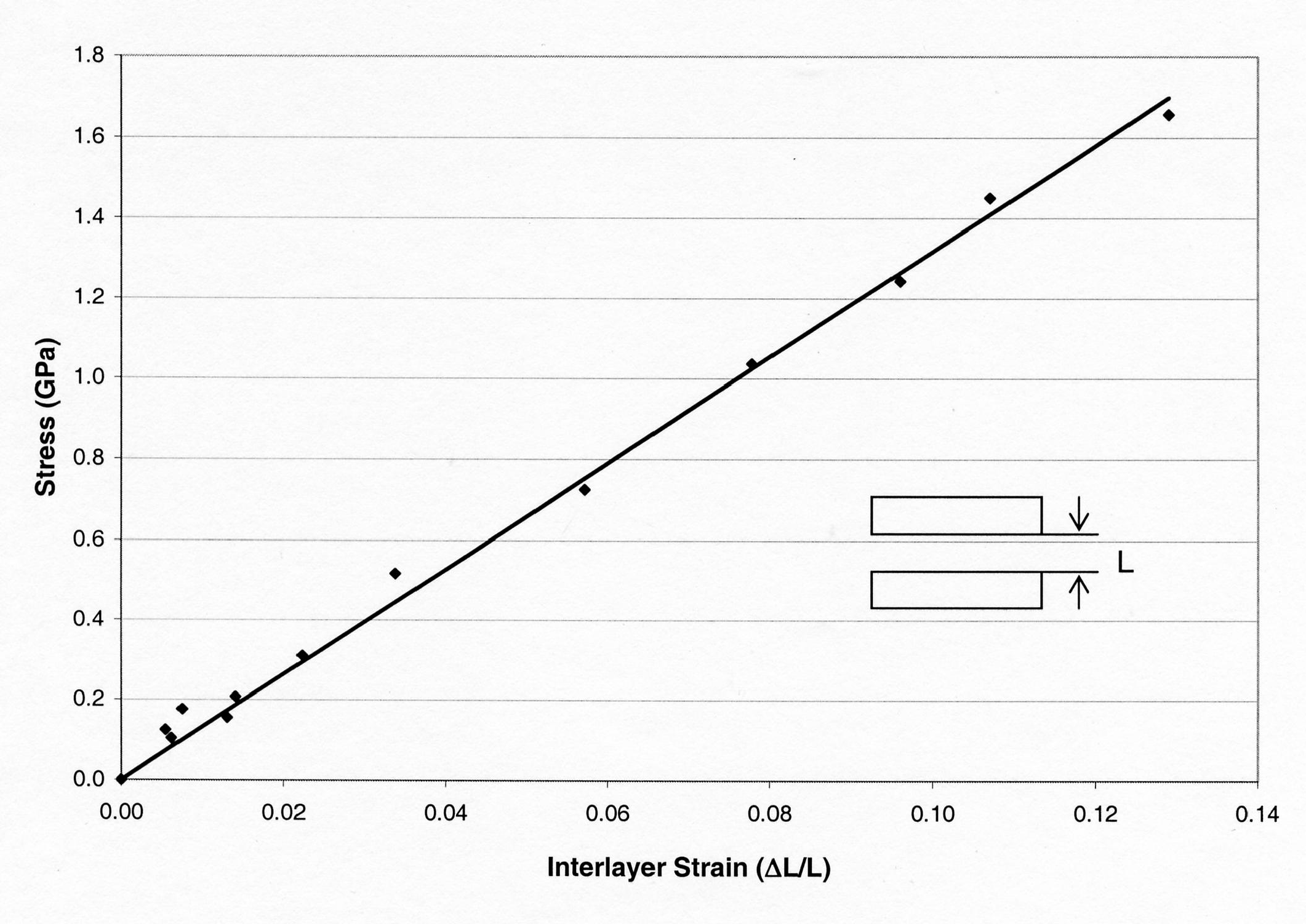
An atomic model for interlayer of pyrophyllite clay has been constructed. CHARMm force field parameters for pyrophyllite clay have been developed. Steered molecular dynamics simulations on dry pyrophyllite clay interlayer were conducted to quantitatively evaluate the stress deformation response of the interlayer. Our results indicate that under applied compressive stress of 0 to 1.65 GPa, the stress deformation response of the interlayer is almost linear. The predominant deformation of the clay model results from deformation of interlayer spacing. Compressive response of individual components, the clay layers and interlayer are found. The modulus of the interlayer and the clay layer is found. In this work, the steered molecular dynamics is shown to be a powerful tool to evaluate quantitative mechanical response of clay interlayers.
Two water layers in the interlayer collapsed into one under a high external stress on clay surfaces.
Interlayer spacing
versus applied stress for sodium montmorillonite with three
monolayers of water in the interlayer.
p
Schmidt, S., Katti, D., Ghosh,
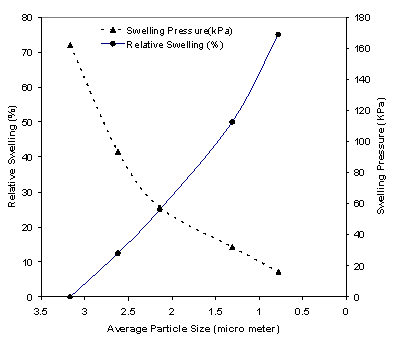
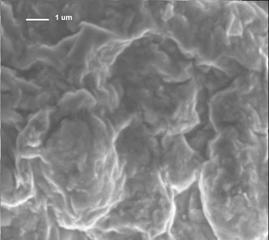
P., and RELATIONSHIP OF SWELLING AND SWELLING PRESSURE ON SILICA-WATER INTERACTIONS IN MONTMORILLONITE Undisturbed clay samples at well defined swelling (0%-75%) were removed from the CUS cell and analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Orientation dependant micro-attenuated total reflectance (ATR) spectroscopic investigations are also conducted on the controlled swelled samples. Significant changes in the silicate (Si-O) stretching region have been observed with changes in swelling and orientation. The band arising from Si-O vibrations when montmorillonite platelets are normal to incident radiation) is most pronounced for the 0% swelled sample and diminishes with swelling. The band associated with perpendicular vibration increases with swelling. Thus intensity of this band increases with misorientation of clay particles. Our results indicate that the reduced particle size as ascertained from SEM cryoimaging, with increased swelling is related to increased misorientation of the clay platelets. At 0% swelling, the clay platelets are most oriented and have largest particle size. The rearrangement of clay platelets as seen in the orientation dependant spectra are a direct result of the breakdown of the clay particles with increased hydration resulting from increased swelling. Katti, K.S., and Katti, D.R., (2006), Relationship of Swelling and Swelling Pressure on Silica-Water Interactions in Montmorillonite, Langmuir, in-press. Coming soon : Results of Discrete Element Modeling
|
|||||