|











| |
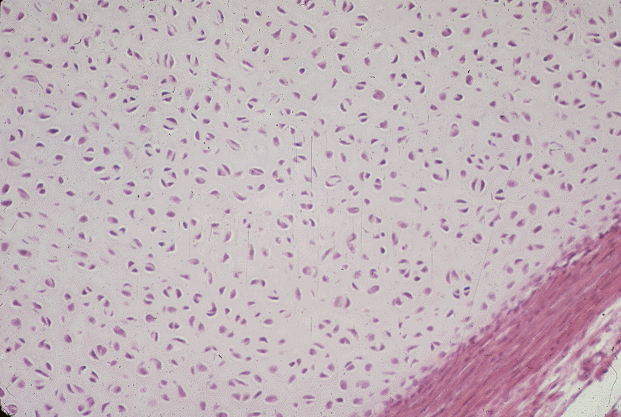
Hyaline
Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage has just a few collagen fibers
embedded in its matrix. It is generally quite smooth, and has a
bluish-white, glass-like appearance grossly. It is found in places
like the rings that hold the trachea open and covering the articular
(joint) surfaces of bones.
|
hyaline cartilage (microscopic)
|
|





