Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of fungicides in single and sequential applications to manage Fusarium head blight (FHB) in barley.
Methods:
Location: NDSU Langdon Research Extension Center
Experimental design: Randomized complete block with split plot arrangement, four replications.
Previous crop: Canola
Cultivars of barley tested: ND Genesis (moderately susceptible/susceptible, released by NDSU) and AAC Synergy (moderately resistant, Syngenta)
Planting: 1.25 million pure live seeds/acre planted on May 25, 2022. A border plot was planted between treated plots to minimize interference from spray drift.
Plot size: Seven rows at six inch spacing, 5 ft. x 20 ft., mowed back to 5 ft. x 16 ft.
Herbicides applied: Axial Bold @15 fl oz/A and Huskie FX @18 fl oz/A were applied on 6/17/2022.
Inoculation: Plots were inoculated by spreading corn spawn inoculum at boot stage (Feekes 9-10) at the rate of 300 g/plot.
Disease development: Supplemental moisture was provided for a month starting from boot to soft dough stage by running overhead irrigation from Feekes 9 to 11.2.5 at the rate of one hour per day to create a conducive environment for FHB development.
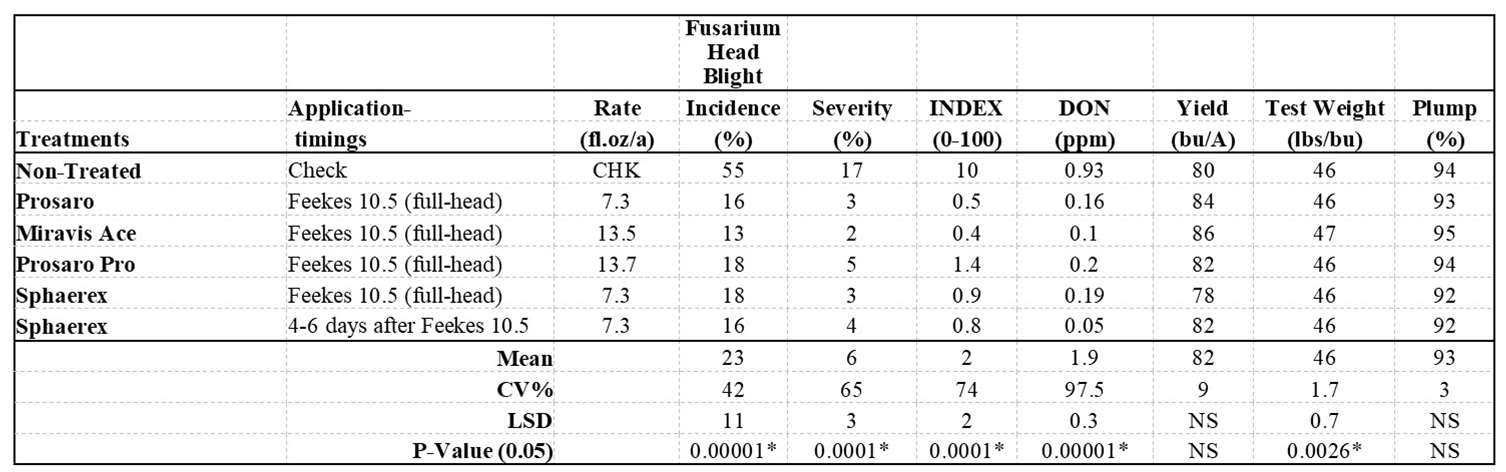
Fungicide treatments: Fungicides were applied with a CO2-pressurized backpack sprayer with a three-nozzle boom (XR-8002) and the water volume used was 20 GPA. Fungicide treatments of Miravis Ace, Prosaro, Prosaro Pro, and Sphaerex were applied at full head emergence stage on July 13 and a treatment of Sphaerex was sprayed 5 days after the full head emergence (July 18) as per protocol requirements. Refer to Table 2 for the treatments, rates and application timings.
Disease assessment: FHB incidence and severity was obtained on fifty random heads showing FHB symptoms excluding two outer rows. FHB head severity was rated using 0-100% scale. FHB index (Index) was calculated using the formula: Index = (SEV*INC)/100.
Harvest: Plots were harvested on August 30 with a small plot combine and the yield was determined at 13.5% moisture.
Data analysis: Statistical analysis was done using GLM in Agrobase Generation II software. Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) was used to compare means at p (α = 0.05).
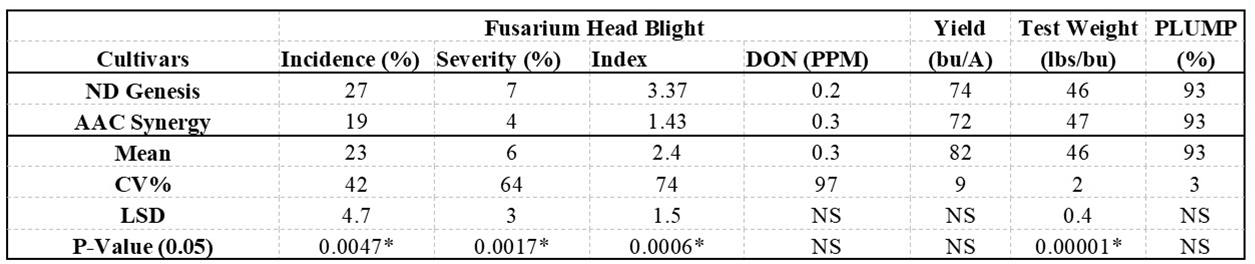
Results: Among the two barley cultivars statistically significant differences were found among the variables of FHB incidence, severity, index and test weight (Table 1). Likewise, there were significant differences in FHB incidence, severity, index, DON, and test weight between non-treated check and the fungicide treatments tested (Table 2). There was a significant interaction effect found between the main plot (cultivars) and the subplot (fungicide) treatments in terms of FHB Index.
Table 1: Mean values of the variables tested on the barley cultivars ND Genesis and AAC Synergy obtained on application of fungicide treatments.
NS: Indicates the variables are statistically non-significant between the cultivars tested.