Limonius californicus (Mannerheim), L. infuscatus (Motschulsky), L. canus LeConte, Hypnoidus bicolor (Eschschultz), Aeolus mellillus (Say), Selatosomus aeripennis (Kirby), S. pruininus (Horn) and others.
Coleoptera: Elateridae
Figure 1. Wireworm adult.
Figure 2. Wireworm larva.
Figure 3. Wireworm plant stand loss.
Figure 4. Wireworm bail trapping
K.W. Wanner, P.B. Beauzay, S.D. Eigenbrode, J.J. Knodel, T.J. Prochaska, G.V.P. Reddy, A.J. Varenhorst and P.M. Wagner
PULSE CROPS INFESTED
Chickpea, field pea and lentil.
IDENTIFICATION
Adult: Figure 1
- Called click beetles because when on their back, they can snap their body and spring 3 to 6 inches high while producing a “click” sound.
- About ½ inch long; light reddish brown to dark black.
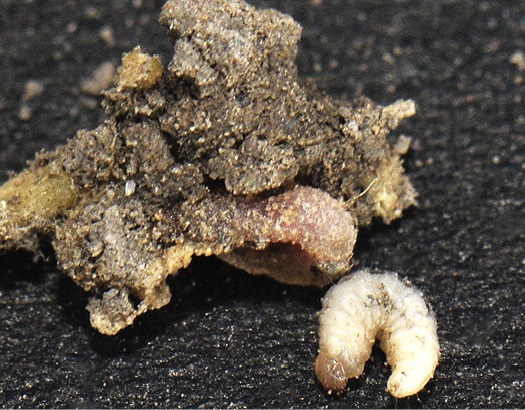
Immature (larva): Figure 2
- Hard, smooth, slender cylindrical or slightly flattened bodies; ¼ to ¾ inch long; creamy white and yellow to a darker orange yellow.
CROP DAMAGE: Figure 3
Wireworms damage crops by feeding on seedlings or the germinating seed. Damaged plants soon wilt and die, resulting in a thinner plant stand.
SCOUTING TIPS
- During crop establishment, scout soil around damaged plants to identify wireworms feeding on the roots.
- Wireworms live below ground.
- Thin, patchy stand establishment after planting is often the first sign of wireworm activity.
- Monitor wireworms by placing attractive baits in the soil at 10 to 20 locations throughout the field or within areas with a history of poor stand establishment. One easy method is to fill a stocking with ½ cup of grain seed, soak the seed in water overnight and bury the stockings 4 to 6 inches deep. After 10 to 14 days, look for wireworms in and around the germinating “bait bag” (Figure 4).
CULTURAL CONTROLS
- Crop rotation and cultivation generally are ineffective.
- Alfalfa is tolerant and wireworm numbers may decline when alfalfa is in the crop rotation.
- Select planting dates that encourage rapid stand growth; larger plants can better tolerate the feeding damage.
ECONOMIC THRESHOLD
- An average of one to two larvae per bait station prior to planting justifies the use of an insecticide seed treatment or infurrow soil insecticide at plant.
OTHER IMPORTANT FACTS
- Wireworm infestations are more likely to become a problem when pulse crops follow grasses, including grain crops, pastures or Conservation Reserve Program land.



















 A.J. Varenhorst, P.M. Wagner, P.B. Beauzay, S.D. Eigenbrode, J.J. Knodel, T.J. Prochaska, G.V.P. Reddy and K.W. Wanner
A.J. Varenhorst, P.M. Wagner, P.B. Beauzay, S.D. Eigenbrode, J.J. Knodel, T.J. Prochaska, G.V.P. Reddy and K.W. Wanner