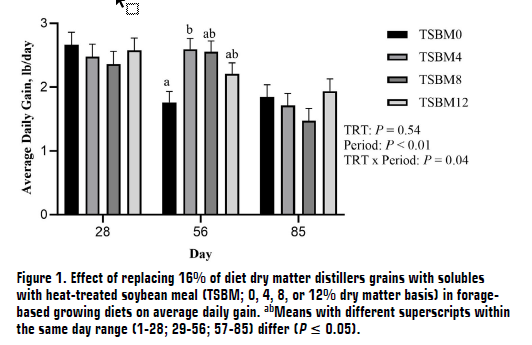
The North Dakota State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all animal procedures. Seventy Angus-based steers (initial BW = 656 ± 36 lb) were utilized in an 85-day growing study at the NDSU Beef Cattle Research Complex in Fargo, North Dakota. Steers originated from the NDSU Central Grasslands Research Extension Center. Steers were provided ad libitum access to feed and water in a monoslope barn with drylot access. Based on 16% inclusion of DDGS, dietary treatments using TSBM were formulated to replace DDGS at increasing inclusion levels of 0 (CON), 4 (TSBM4), 8 (TSBM8), and 12% (TSBM12) on a dry matter (DM) basis (Table 1). Diets were formulated using the empirical solutions model of the Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements Model 2016 (version 1.0.37.15; NASEM, 2016) to increase metabolizable protein and lysine as the inclusion of TSBM increased in the diet. Lysine requirements in the formulated diets were predicted to be deficient for TSBM0 and TSBM4 treatments and in excess for TSBM8 and TSBM12 treatments. In contrast, the metabolizable protein requirement was sufficient for all treatments (Table 2).
Prior to initiation of the study, steers were limit-fed a common diet containing 40% corn silage, 57% oat hay, and 3% dry meal supplement at 1.8% BW for five days followed by three days of weighing to minimize gut fill variation (Watson et al., 2013). The average of the 3-day weights served as the initial BW. Steers were blocked by weight into light (initial BW = 617 ± 14 lb), medium (initial BW = 653 ± 10 lb), and heavy (initial BW = 698 ± 18 lb) blocks and assigned randomly to treatments. The 3-day weight process was repeated at the end of the study to measure the ending BW. On day 0, steers were implanted with 80 mg of trenbolone acetate and 16 mg of estradiol (Revalor®-IS, Merck Animal Health, Summit, NJ). Body weights and blood were collected every 28 days. Blood was collected via jugular venipuncture, processed into plasma and serum samples, and stored at -4ºC until further analysis. Individual daily feed intake was measured using an automated feed system (Insentec Roughage Intake Control, Hokofarm B. V., Marknesse, The Netherlands).
Dietary DM was determined weekly by sampling ingredients and oven-drying at 60ºC for 48 hours. Weekly ingredient samples were collected and ground through a 1-mm screen using a Wiley Mill grinder (Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ). Ground samples were composited into 4-week intervals. Composited ingredient samples were analyzed for laboratory DM, crude protein (CP), organic matter (OM), acid detergent fiber (ADF), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), starch, fat, calcium (C), and phosphorus (P).
Data were analyzed as a generalized randomized block design utilizing the MIXED procedure of SAS (SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, NC) with treatment (n = 4), period (n = 3), and treatment × period interaction as fixed effects, initial BW as a fixed covariate, and period considered a repeated measure using the unstructured variance-covariance structure. Preplanned pairwise comparisons of treatment within period were evaluated and significant model effects (P ≤ 0.05) were adjusted using the Tukey-Kramer methods. Model residual plots were evaluated to ensure mixed procedure assumptions were met and necessary outliers were removed.
Table 1. Experimental diets.
Table 2. Nutrient composition of the experiment diets.