Two experiments were conducted to evaluate the impacts of feeding a vitamin/mineral supplement to beef heifers throughout gestation on concentrations of immunoglobulin (Ig) in colostrum and in calf serum 24 h after consumption of maternal colostrum (Exp. 1) or a colostrum replacement product (Exp. 2). Angus-based heifers (n = 72, 14 to 15 months of age, initial body weight [BW] = 838.6 ± 111.47 pounds [lbs]) were managed in an individual feeding system (American Calan; Northwood, NH) at the NDSU Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center (ANPC; Fargo, ND). Heifers were randomly assigned to receive either the basal diet targeting gain of 1 lb/heifer/day (CON; n = 36) or the basal diet plus a loose product vitamin/mineral supplement (Table 1; Purina Wind and Rain Storm All-Season 7.5 Complete, Land O’Lakes, Inc., Arden Hills, MN) top-dressed on the total mixed ration (TMR) at a rate of 4 oz/heifer/day (VTM; n = 36). All heifers were subjected to a 7-day Select-Synch + CIDR estrus synchronization protocol and bred via artificial insemination (AI) to female-sexed semen from a single sire. Transrectal ultrasonography was conducted to determine pregnancies at day 35 post-insemination, and fetal sex was determined at day 65 after AI to confirm pregnancies with female fetuses.
For Exp. 1, diet treatments began at the time of AI. Heifers becoming pregnant with female fetuses after first service AI (CON, n = 14; VTM, n = 17) were transported to the NDSU Beef Cattle Research Complex (BCRC; Fargo, ND), adapted to the Insentec Roughage Intake Control Feeding System (Hokofarm B.V., Marknesse, The Netherlands), and diet treatments were continued throughout pregnancy. The basal diet for heifers on Exp. 1 consisted of corn silage; alfalfa, millet, or prairie hay; and dried corn distillers grains plus solubles. During late-gestation, feed deliveries were adapted to provide ad libitum feed intakes through calving. At calving, heifer calves were allowed to nurse their dams and remained alongside their dams until weaning.
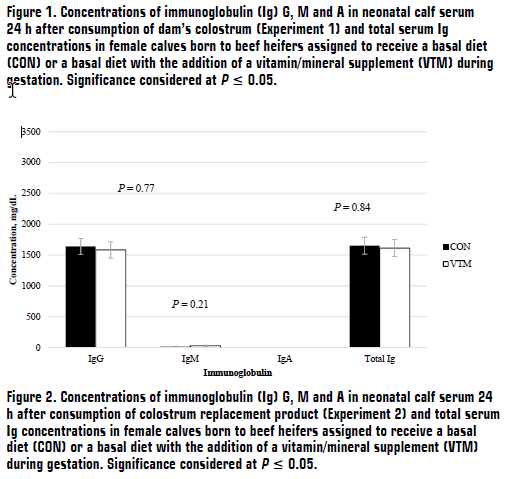
For Exp. 2, heifers that did not become pregnant to first-service AI (CON, n = 19; VTM, n = 18) were synchronized for estrus and rebred via AI 60 days after initial dietary treatments began and continued treatments throughout pregnancy at the ANPC. The basal diet consisted of grass hay, corn silage, and dried corn distillers grains plus solubles. During late-gestation, pregnant heifers were transported to the BCRC, and feed deliveries of the basal diet were adapted to provide ad libitum intakes through calving. The basal diet consisted of corn silage, alfalfa hay, dried corn distillers grains plus solubles, and a corn-based premix. Heifer calves born (CON, n = 7; VTM, n = 7) were removed from their dams at birth, relocated to individual pens, and fed 1.5 liters of colostrum replacer containing 150 g globulin protein (Lifeline Rescue High-Level Colostrum Replacer; APC, Inc; Ankeny, IA) via an esophageal feeder within 2 h of birth. Every 12 h, calves were fed 2 liters of milk replacer (Duralife Optimal Non-Medicated Calf Milk Replacer; Duralife; Fort Worth, TX) via an esophageal feeder.
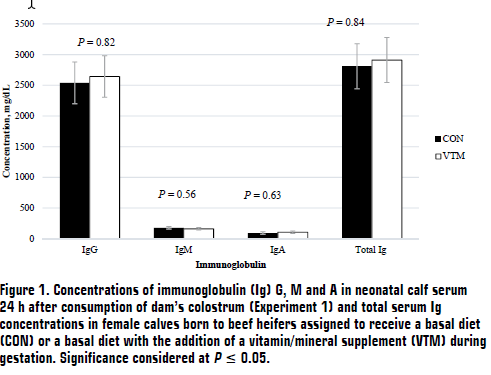
In both experiments, samples of colostrum from the dam at calving were obtained by completely milking the rear-right quarter of the udder using a portable milk machine (InterPuls, Albinea, IT). Blood samples were collected from calves pre-suckling (within 2 h of birth) and 24 h after colostrum consumption via jugular venipuncture. Concentrations of immunoglobulin G (IgG), M (IgM), and A (IgA) were quantified in colostrum and serum (pre-suckling and 24 h post-suckling) using bovine radial immunodiffusion plate kits (Triple J Farms; Bellingham, WA).
For Exp. 1, blood was collected at numerous time points relative to vaccination at 24 h of age, pasture turn out, and at weaning to assess antibody titer response to vaccination. Blood samples were collected on the day of vaccination (24 h of age, pasture turnout, and 7 d pre-weaning) and 14 days following vaccination, totaling six blood collection time points. At 24 h of age, vaccinations administered included protection against respiratory viruses (IBR, PI3, and BRSV) and clostridial diseases. At the time of pasture turn out on native range pasture, calves were administered vaccinations to protect against respiratory viruses (IBR, PI3, BRSV, BVDV-1, BCDV-2, and Mannheimia haemolytica), clostridial diseases, pinkeye, and an anthelmintic was administered. At 7 d prior to weaning, calves received vaccinations to protect against respiratory viruses (IBR, PI3, BRSV, BVDV-1, BVDV-2, and Mannheimia haemolytica), clostridial diseases, and pinkeye.
Blood samples were allowed to clot after collection and placed on ice until centrifugation. Samples were centrifuged at 1,500 × g at 4º for 20 minutes, aliquoted into 2-mL plastic microtubes, and stored at -20º until analysis. Serum was analyzed at Oklahoma State University Animal Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (Stillwater, OK) via serum neutralization (SN) for detection of antibodies for BVDV Type 1 and Type 2, BRSV, IBR, and PI3. Data for both experiments were analyzed for the effect of treatment using the MIXED procedure in SAS. Significance was considered at P ≤ 0.05.
Table 1. Composition of VTM supplement1 provided to beef heifers at breeding until calving2; company guaranteed analysis.