Nonparenteral Medication Administration
Select a Skill:
- » Applying Topical Medications
- » Applying an Estrogen Patch and Nitroglycerin Ointment
- » Administering Eye Medications
- » Administering Ear Medications
- » Using a Metered-Dose Inhaler
- » Using a Dry Powder Inhaler
- » Inserting a Rectal Suppository
Take the Review Test:
Safety
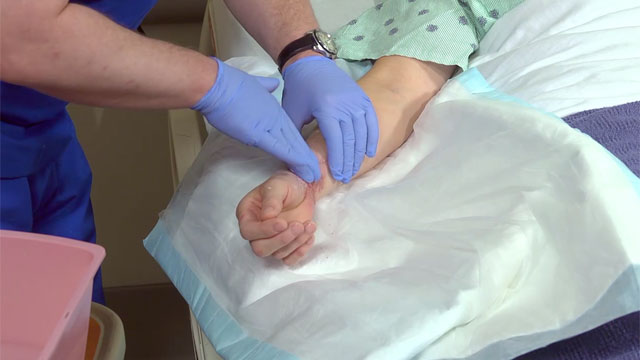
- Ensure that the six rights of medication administration are followed: right medication, right dose, right patient, right route, right time, and right documentation.
- Be aware that a topical medication can have systematic effects if it is absorbed through the skin and are more likely to occur if the skin is thin, drug concentration is high, contact with the skin is prolonged, or the drug is applied to nonintact skin.
- To protect yourself from accidental exposures, wear gloves or use an applicator when applying topical medications.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendation for application to ensure proper penetration and absorption.
- Avoid applying a heat source, such as a heating pad, over a transdermal patch, because doing so can increase the rate of absorption and have serious adverse effects.
- Never apply estrogen transdermal patches on or around breast tissue.
- Use a felt-tip pen or other soft-tip pen (not a ball point pen) to write the date and time on a transdermal patch. Ball-point ink may interfere with medication absorption.
- For the safety of patients, other adults, pets, and children, instruct the patient to wrap applicators, used patches, and similar materials that may contain medication and place them in cardboard or plastic containers for disposal.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
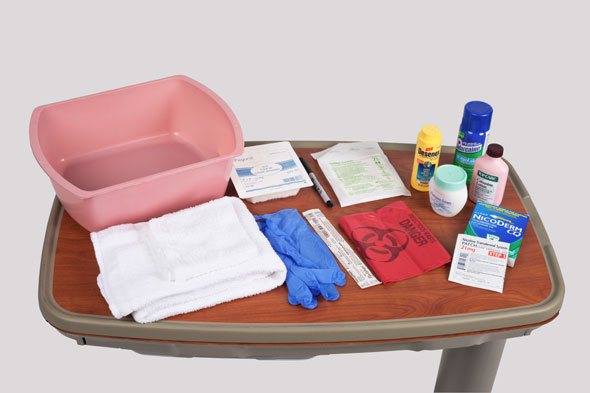
Ordered medication - Cream
Ordered medication - Patch
Ordered medication - Spray
Ordered medication - Suspension-based lotion
Ordered medication - Powder
Clean gloves (for intact skin)
Sterile gloves (for nonintact skin)
Tongue blades (sterile)
Basin
Washcloth and towel
Sterile 4x4 dressing (if needed)
Felt-tip pen
Biohazard disposal bag (optional)
Delegation
Administration of topical medication may not be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). If the facility policy allows, the task of applying certain lotions and ointments to soothe irritated skin or to provide perineal protection may be delegated to NAP. Be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Expected therapeutic effects and potential side effects that should be reported to the nurse.
Preparation
- Check the accuracy and completeness of the medication administration record (MAR) against the health care provider’s medication order.
- Note the patient’s allergies.
- Determine the amount of topical agent required for application. Read the manufacturer’s application instructions carefully.
- Observe the six rights of medication administration: right medication, right dose, right patient, right route, right time, and right documentation. (For details, see the video skill "Ensuring the Six Rights of Medication Administration.")
- Prepare medications for application. Check the medication's label against MAR twice. Preparation usually involves taking the bottle, tube of lotion, cream, ointment or patch out of storage and to the patient's room. Check the expiration date.
Follow-up
- Ask the patient or family member to name the medication and state its action, purpose, dosage, schedule, and side effects.
- Have the patient keep a diary of medication doses and locations of application.
- Observe the patient or caregiver applying the topical medication. Provide guidance as needed.
- Inspect the skin between applications, noting therapeutic effects as well as any redness, irritation, blisters, or oozing.
- Report the patient's response, side effects, and/or withheld doses to the nurse in charge or to the health care provider.
- Discuss reasons for noncompliance and possible alternatives if the patient is unable to explain information about the drug or does not administer it as prescribed.
Documentation
- Document the condition of the skin before topical medication is applied.
- Record the time of administration, type and strength of medication applied, and application site in the MAR immediately after administration. For hard copy documentation, include time and initials or signature per institutional policy.
- Record patient teaching and validation of the patient's understanding.
- Record the reason for any withheld medication and follow facility policy for noting withheld doses.
- Record the indication for the medication administration as well as therapeutic response.
Review Questions
1. The nurse is preparing to apply a topical oil-based medication to a patient's forearms. What should the nurse do to minimize the risk of contamination during the application?
 Encourage the patient to self-apply the medication
Encourage the patient to self-apply the medication Wear treatment gloves during the entire application process
Wear treatment gloves during the entire application process Change gloves between prepping the skin and applying the medication
Change gloves between prepping the skin and applying the medication Perform effective hand hygiene before and after application
Perform effective hand hygiene before and after application
2. Which of the following discharge instructions would be most important in ensuring the safety of a patient who will need to apply a dermal patch daily at home?
 Apply sufficient pressure to the edges of the patch to ensure adequate adherence.
Apply sufficient pressure to the edges of the patch to ensure adequate adherence.  Avoid using a heating pad on or near the application site.
Avoid using a heating pad on or near the application site.  Pat the application site dry before applying the patch.
Pat the application site dry before applying the patch.  Reapply the patch to the same site each time to enhance absorption.
Reapply the patch to the same site each time to enhance absorption.
3. Which of the following is not taken into consideration when determining the appropriate amount of a topical medication to be applied to the skin?
 Size of the skin site
Size of the skin site Other medications the patient is taking
Other medications the patient is taking  Manufacturer’s instructions for application of the product
Manufacturer’s instructions for application of the product  Health care provider’s order
Health care provider’s order
4. The nurse is preparing to discharge a patient after instructing her in self-application of a topical medication. What is the best way for the nurse to ensure that the patient understands the instructions?
 Discuss with the patient the most common errors in application
Discuss with the patient the most common errors in application  Review the material several times with the patient and family
Review the material several times with the patient and family  Allow the patient to apply the topical medication and provide feedback on technique
Allow the patient to apply the topical medication and provide feedback on technique  Give the patient printed materials for later reference
Give the patient printed materials for later reference
5. The nurse is applying a topical antibiotic and dressing to a burn on the hand of a patient being treated as an outpatient. What is the most important thing the nurse can do to minimize the risk of infection?
 Evaluate the patient's ability to recognize the signs and symptoms of infection
Evaluate the patient's ability to recognize the signs and symptoms of infection  Perform effective hand hygiene before and after the application
Perform effective hand hygiene before and after the application  Instruct the patient not to change the dressing between visits
Instruct the patient not to change the dressing between visits  Apply the medication using sterile technique
Apply the medication using sterile technique
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.


