Nonparenteral Medication Administration
Select a Skill:
- » Applying Topical Medications
- » Applying an Estrogen Patch and Nitroglycerin Ointment
- » Administering Eye Medications
- » Administering Ear Medications
- » Using a Metered-Dose Inhaler
- » Using a Dry Powder Inhaler
- » Inserting a Rectal Suppository
Take the Review Test:

Safety
- If the patient wishes to self-administer the suppository, be certain he knows that the foil wrapper must be removed before insertion.
- Rectal medications are contraindicated in patients with recent surgery on rectum, bowel, or prostate gland, as well as patients with rectal bleeding, prolapse, diarrhea, and very low platelet counts.
- Monitor the patient's heart rate. Unintended vagal stimulation may occur during insertion, causing bradycardia in some patients.
- Be aware that medication instilled rectally is absorbed rapidly through the highly vascular rectal mucosa and may have systemic side effects, such as hypotension. Monitor the patient's vital signs.
- Insert the rounded end of the suppository first, to prevent anal trauma.
- Do not cut a suppository into sections to divide doses; this may result in an inaccurate dosing.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
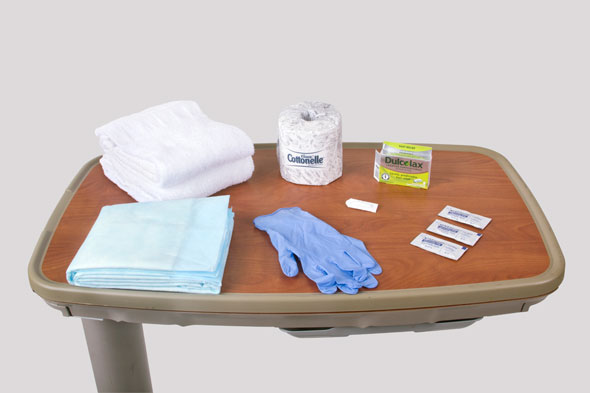
Rectal suppository
Water-soluable lubricating jelly
Clean gloves
Tissue
Waterproof pad
Towels or drape
Delegation
The skill of administering a rectal suppository cannot be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). Be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Review the expected therapeutic effects (bowel movement, reduced nausea, fever, or pain), as well as potential medication side effects (rectal discharge, pain, rectal bleeding) that NAP should report to the nurse.
Preparation
- Check the accuracy and completeness of each medication administration record (MAR) against the health care provider’s medication order. Confirm the patient’s name, the drug and dosage, the route of administration, and the time of administration. Clarify incomplete or unclear orders with the health care provider.
- Note patient allergies.
- Observe the six rights of medication administration: right medication, right dose, right patient, right route, right time, and right documentation. (For details, see the video skill "Ensuring the Six Rights of Medication Administration.")
- Assess the patient for contraindications for a suppository, including diarrhea, rectal bleeding, rectal, bowel or prostrate surgery, and/or cardiac problems.
- Assess indications for receiving the rectal medication such as fever, constipation, pain, or nausea.
- Determine the patient's ability to hold the suppository.
- Assess the patient’s interest in self-administration of the rectal suppository.
Follow-up
- Return to the bedside within 5 minutes to determine if the suppository was expelled.
- Ask if the patient experienced localized anal or rectal discomfort during insertion.
- Observe for and document the patient’s response to the supposity, such as relief from symptoms (constipation, fever, pain) for which medication was given.
- Document and report side effects from administration of the rectal suppository.
Documentation
- Document the medication, dose, and time of drug administration on the MAR immediately after administration, not before. Include your initials or signature.
- Record patient teaching and validation of the patient's understanding and self-administration of the suppository, if applicable.
- Document the patient response to the medication both desired (relief of constipation) as well as side effects such as cramping.
Review Questions
1. A female nurse is preparing to administer a rectal suppository to a male patient. The patient says, "This is so embarrassing. Is this really necessary?” What is the most appropriate response?
 "I can see if the doctor will order an oral medication."
"I can see if the doctor will order an oral medication."  "How about if I show you how to insert the suppository yourself?"
"How about if I show you how to insert the suppository yourself?"  "I will make sure that you are well covered. I promise."
"I will make sure that you are well covered. I promise."  "This will make you feel so much better.”
"This will make you feel so much better.”
2. The nurse is preparing to administer a rectal suppository to an elderly patient. Which step best protects the patient's safety?
 Ask the patient to take deep, slow breaths as the suppository is being inserted.
Ask the patient to take deep, slow breaths as the suppository is being inserted.  Insert the suppository two inches into the rectum.
Insert the suppository two inches into the rectum.  Place the patient in the left side-lying position with the top leg flexed.
Place the patient in the left side-lying position with the top leg flexed.  Instruct the patient to use the call button for assistance to the bathroom.
Instruct the patient to use the call button for assistance to the bathroom.
3. Which statement made by a nurse best illustrates an understanding of the role of nursing assistive personnel (NAP) in administering a rectal suppository?
 "Find out whether the patient is capable of inserting the suppository."
"Find out whether the patient is capable of inserting the suppository."  "Please tell the patient to report if any rectal bleeding occurs."
"Please tell the patient to report if any rectal bleeding occurs."  "Be sure to let me know if the patient has a bowel movement."
"Be sure to let me know if the patient has a bowel movement."  "Remember to lubricate the suppository."
"Remember to lubricate the suppository."
4. After administering a rectal suppository for constipation, the nurse will monitor for all of the following responses except which one?
5. The nurse should question a provider's order to insert a suppository into the rectum of a patient with which condition?
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.


