Injections
Select a Skill:
- » Preparing Injections from an Ampule
- » Preparing Injections from a Vial
- » Preparing and Administering Insulin
- » Drawing up More Than One Type of Insulin
- » Administering Intradermal Injections
- » Administering Subcutaneous Injections
- » Administering Intramuscular Injections
Take the Review Test:

Safety
Follow the Six Rights of Medication Administration: right medication, right dose, right patient, right route, right time, and right documentation.
- Do not aspirate during intradermal injection, because the dermis is relatively avascular.
- Wear clean gloves during intradermal injection to limit contact with bodily fluids.
- Use strict asepsis when preparing and administering an intradermal injection.
- Observe a “No Interrutption Zone” while preparing medications.
- The skin of older adults is less elastic and must be held taut to ensure correct administration of the intradermal injection.
- Stay with the patient for several minutes after providing the injection to watch for signs of an allergic reaction. Dyspnea, wheezing, and circulatory collapse signify severe anaphylactic reaction.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
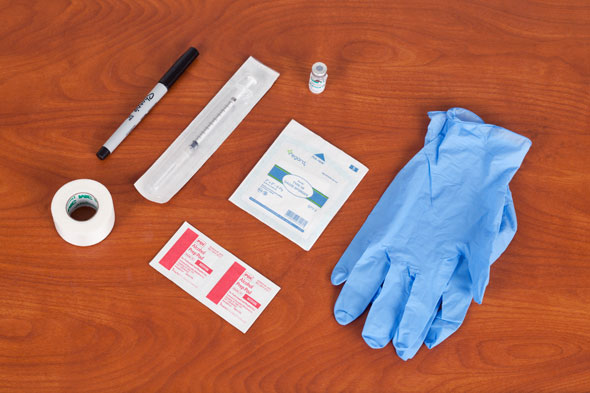
Syringe: 1-mL tuberculin syringe with 25-gauge or 27-gauge, 3/8 to 5/8 inch needle
Small gauze pad
Alcohol swab
Vial or ampule of medication
Clean gloves
Marker (skin safe)
Tape (to label syring, if necessary)
Delegation
The skill of administering an intradermal injection may not be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). Be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Review the potential side effects of the medication.
- Instruct NAP to report such side effects to you.
Preparation
- Check the accuracy and completeness of each medication administration record (MAR) against the health care provider’s orders. Confirm the patient’s name, medication name, dosage, route of administration, and time of administration. Clarify incomplete or unclear orders with the health care provider.
- Note if the patient has allergies.
- Review the medication reference information about expected reactions to skin tests for specific allergens or medications, and note the appropriate time to read the site.
- Assess the patient’s history of allergies including the known allergen types, and the patient’s typical allergic reaction.
- Ascertain any contraindications to intradermal injections. Assess for a history of severe adverse reactions or necrosis following previous intradermal injection.
- Determine if the patient understands the reason for the skin test and knows what responses to report.
- Prepare the medication for injection. Check the label of the medication against the MAR two times. A third check will take place at the bedside. Note the expiration date of the medication.
- If the syringe is prepared away from the patient’s bedside, label it with the name and dose of medication in the syringe.
Follow-up
- Return to the patient’s room in 15 to 30 minutes, and ask her if she feels any acute pain, burning, numbness, or tingling at the injection site.
- Ask the patient to discuss the implications of skin testing and the signs of hypersensitivity.
- Inspect the bleb. As an option, use a skin pencil and draw a circle around the perimeter of the injection site.
- Read a tuberculin (TB) test site at 48 to 72 hours; look for induration—a hard, dense, raised area—around the injection site. The test is positive if you see:
- An induration of 15 mm or more in a patient with no known risk factors for TB
- An induration of 10 mm or more in a patient who is a recent immigrant, injection drug user, resident or employee in a high-risk setting, patient with a specified chronic illness, a child younger than 4 years of age, or an infant, child, or adolescent who has been exposed to a high-risk adult.
- An induration of 5 mm or more in a patient who is human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive, has fibrotic changes on a chest x-ray consistent with a previous TB infection, has had an organ transplant, or has immunosuppression.
Documentation
- Record the drug, dose, route, site, time, and date on the MAR immediately after administering the intradermal injection, and not before. For hard-copy documentation, include the time and your initials or signature per agency policy.
- Record the location of the intradermal injection and the appearance of the patient’s skin afterward.
- Document any adverse effects according to your agency’s policy, and report them to the health care provider.
- Record any patient teaching, validation of understanding, and the patient’s response to the intradermal injection.
Review Questions
1. When administering an intradermal injection, which outcome would require the nurse to withdraw the needle and begin again?
 Aspiration of blood prior to injecting the medication
Aspiration of blood prior to injecting the medication Inability to feel resistance when injecting the medication
Inability to feel resistance when injecting the medication Formation of a 6-mm bleb at the injection site
Formation of a 6-mm bleb at the injection site Appearance of a lesion resembling a mosquito bite at the injection site
Appearance of a lesion resembling a mosquito bite at the injection site
2. Which statement might the nurse make to nursing assistive personnel (NAP) when caring for a patient who is prescribed an intradermal injection?
 “Be sure to wear clean gloves during the injection.”
“Be sure to wear clean gloves during the injection.” “Tell him it’s OK; the site should look like a mosquito bite.”
“Tell him it’s OK; the site should look like a mosquito bite.” “Immediately report any patient complaints of itching or dyspnea.”
“Immediately report any patient complaints of itching or dyspnea.” “Remind the patient to come back in 48 to 72 hours so we can evaluate the site.”
“Remind the patient to come back in 48 to 72 hours so we can evaluate the site.”
3. Which finding tells the nurse that a patient may have had a positive reaction to a tuberculin test?
 A raised wheal the size of a mosquito bite
A raised wheal the size of a mosquito bite A bruised area 10 mm or greater in diameter
A bruised area 10 mm or greater in diameter A hard, raised area 15 mm or greater in diameter
A hard, raised area 15 mm or greater in diameter A flat, reddened area 5 mm or greater in diameter
A flat, reddened area 5 mm or greater in diameter
4. In which site would it be inappropriate to administer an intradermal injection?
 Lower abdomen of an obese patient
Lower abdomen of an obese patient Upper back of a patient who is on bed rest
Upper back of a patient who is on bed rest Right deltoid of a high school softball pitcher
Right deltoid of a high school softball pitcher Left forearm of a patient with right-sided weakness
Left forearm of a patient with right-sided weakness
5. How can the nurse determine that the needle tip for an intradermal injection is in the dermis?
 A bleb the size of a mosquito bite will appear.
A bleb the size of a mosquito bite will appear. The needle will enter at a 5- to 15-degree angle.
The needle will enter at a 5- to 15-degree angle. The bulge of the needle tip will be visible through the skin.
The bulge of the needle tip will be visible through the skin. The needle will penetrate through the epidermis to a depth of about ⅛ inch.
The needle will penetrate through the epidermis to a depth of about ⅛ inch.
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.


