Injections
Select a Skill:
- » Preparing Injections from an Ampule
- » Preparing Injections from a Vial
- » Preparing and Administering Insulin
- » Drawing up More Than One Type of Insulin
- » Administering Intradermal Injections
- » Administering Subcutaneous Injections
- » Administering Intramuscular Injections
Take the Review Test:

Safety
Ensure that the Six Rights of Medication Administration are observed: right medication, right dose, right patient, right route, right time, and right documentation. Follow the principles of sterile technique when administering an intramuscular injection.
- Wear gloves to reduce the risk of contact with bloodborne pathogens.
- Do not use an injection site in an area with bruising, induration, muscular atrophy, reduced blood flow, or signs of infection.
- Ensure that the position for injection is not contraindicated by the patient’s medical condition.
- To prevent administration of the medication directly into a blood vessel, aspirate when giving all intramuscular injections except vaccines.
- Rotate intramuscular injection sites to decrease the risk of tissue hypertrophy.
- In older adults and thin patients, do not administer a volume of more than 2 mL by intramuscular injection. In infants and small children, do not administer a volume of more than 1 mL.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
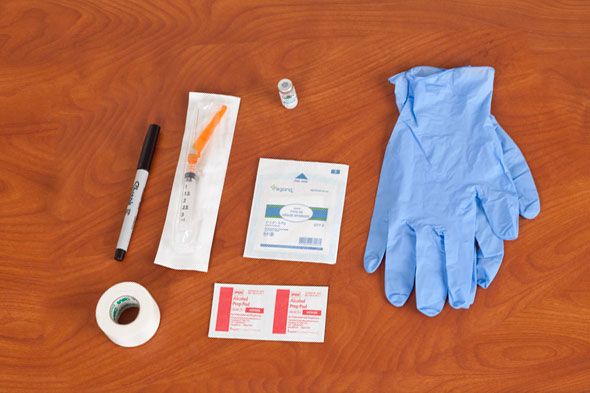
3 mL syringe with 21-gauge, 1 1/2 inch needle with safety device
Small gauze pad
Alcohol swab
Vial or ampule of medication
Clean gloves
Marker
Tape
Delegation
The skill of administering an intramuscular injection cannot be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). Before delegating related skills, be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Outline expected therapeutic effects and potential side effects of the medication, and instruct NAP when to report them.
- Instruct NAP to report any change in the patient’s condition.
Preparation
- Check the accuracy and completeness of the medication administration record (MAR) or computer printout against the prescriber’s written medication orders. Confirm the patient’s name, medication name and dosage, route of administration, and time of administration. Clarify incomplete or unclear orders with the health care provider.
- Note if the patient has allergies.
- Review the medication reference information for medication action, purpose, normal dose, side effects, time of peak action and nursing implications.
- Review the patient’s previous verbal and nonverbal responses to the injection.
- Assess for contraindications to intramuscular injections, such as muscle atrophy, reduced blood flow, and circulatory shock.
- Review the MAR to note the locations of previous injections.
- When drawing up medication for injection away from the patient’s bedside, label the syringe with the name and amount of medication it contains.
Follow-up
- Return to the room 15 to 30 minutes after the injection; ask the patient if he or she feels any acute pain, burning, numbness, or tingling at the injection site.
- Inspect the site, noting any bruising or induration. Apply a warm compress if necessary.
- Observe the patient’s therapeutic response to the medication at times that correlate with the onset, peak, and duration of the medication. Watch for any adverse effects.
- Confirm the patient’s understanding of the medication’s purpose, action, possible side effects, and self-administration technique if applicable.
Documentation
- Document the medication administered by intramuscular injection, its concentration, dosage or strength, time, date, and site of administration. This documentation must be made on the MAR immediately after administration, not before.
- Document any patient teaching and validation of the patient’s understanding.
- Document and report to the health care provider any withheld doses and/or the patient’s response to the medication, including any side effects.
Review Questions
1. Which action by the nurse ensures patient safety when administering an intramuscular injection?
 Putting on clean gloves before administration
Putting on clean gloves before administration Rotating injection sites
Rotating injection sites Aspirating for blood return when administering a vaccine
Aspirating for blood return when administering a vaccine Injecting the medication quickly
Injecting the medication quickly
2. When preparing an intramuscular injection, what can the nurse do to reduce the patient’s risk for infection?
 Wear clean gloves.
Wear clean gloves. Use a 3-mL syringe.
Use a 3-mL syringe. Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab.
Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab. Massage the injection site.
Massage the injection site.
3. What can the nurse do to minimize the patient’s risk for injury when delivering an intramuscular injection?
 Instruct the patient to relax.
Instruct the patient to relax. Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle.
Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle. Pull back on the plunger after inserting the needle.
Pull back on the plunger after inserting the needle. Pull the skin taut at the injection site when inserting the needle.
Pull the skin taut at the injection site when inserting the needle.
4. Which site is most commonly used for intramuscular injections?
5. Which action by the nurse helps to ensure that the medication is delivered into the muscle when administering an intramuscular injection?
 Using a 1-inch needle
Using a 1-inch needle Inserting the needle at a 45- to 60-degree angle
Inserting the needle at a 45- to 60-degree angle Withdrawing the needle immediately after delivering the medication
Withdrawing the needle immediately after delivering the medication Aspirating for blood return before injection medication
Aspirating for blood return before injection medication
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.


