Respiratory Care and Suctioning
Select a Skill:
- » Ensuring Oxygen Safety
- » Setting Oxygen Flow Rates
- » Applying a Nasal Cannula or Face Mask
- » Maintaining an Airway
- » Providing Tracheostomy Care
- » Performing Oropharyngeal Suctioning
- » Performing Nasotracheal and Nasopharyngeal Suctioning
Take the Review Test:

Safety
- Treat oxygen therapy as a medication. Do not substitute oxygen for any other treatment. Use it only when indicated, at the flow rate ordered.
- Ensure that the patient has no contraindication to oxygen therapy, such as elevated PaCO2 (hypercarbia), which puts the patient at increased risk for respiratory failure.
- Do not interrupt oxygen therapy during patient transport.
- A plastic face mask with a reservoir bag and a Venturi mask will deliver 60% to 90% oxygen at appropriate flow rates. The reservoir bag of this oxygen mask maintains a high-concentration oxygen supply. Frequently inspect the bag to make sure it is fully inflated. If it is not fully inflated, the patient breathes in large amounts of exhaled carbon dioxide.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
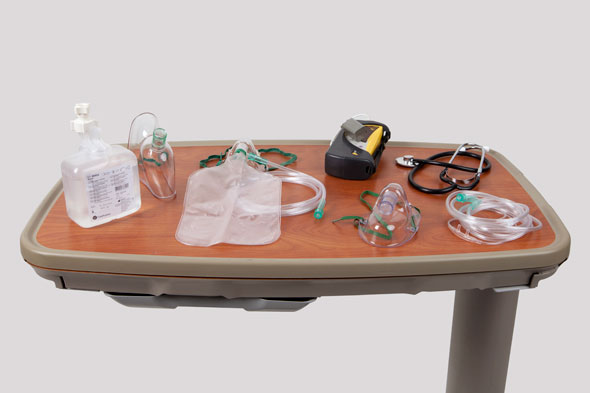
Stethoscope
Pulse oximeter
Nasal cannula and tubing
Nonrebreathing mask and tubing
Venturi mask
Face tent
Humidifier set-up for oxygen
Delegation
The skills of initiating and adjusting oxygen flow may not be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP); the nurse is responsible for assessing the patient’s respiratory system and response to oxygen therapy, and for setting up the oxygen delivery device and adjusting the oxygen delivery rate. The skill of applying a nasal cannula or oxygen mask may be delegated to NAP. Be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Review the procedure for safely adjusting the device, such as loosening the strap on the oxygen cannula or mask.
- Instruct NAP to inform you immediately about any changes in vital signs; changes in level of consciousness; skin irritation from the cannula, mask, or straps; or patient complaints of pain or breathlessness.
Preparation
- Assess the patient’s respiratory status, including the following:
- Symmetry of chest wall expansion
- Chest wall abnormalities, such as kyphosis
- Temporary conditions that can affect ventilation, such as pregnancy or trauma
- Respiratory rate and depth
- Sputum production
- Lung sounds
- Signs and symptoms associated with hypoxia
- Observe the patient for a patent airway, and remove airway secretions by having the patient cough and expectorate mucous, or by suctioning.
- If available, note the patient’s most recent ABG results or SpO2 value.
- Review the patient’s medical record for the medical order for oxygen, noting the delivery method, flow rate, and duration of oxygen therapy.
- Explain the procedure to the patient and family.
Follow-up
- Use pulse oximetry to monitor the patient’s response to changes in the oxygen flow rate. NOTE: Monitor ABGs when ordered; however, ABG measurement is an invasive procedure and is therefore not frequently ordered.
- Observe the patient for decreased anxiety, improved level of consciousness and cognitive abilities, diminished fatigue, absence of dizziness, decreased respiratory rate, improved color, improved oxygen saturation, and a return to the his or her baseline vital signs.
- Assess the adequacy of oxygen flow each shift.
- Observe the patient’s external ears, the bridge of the nose, nares, and nasal mucous membranes for evidence of skin breakdown.
- If oxygen therapy continues after discharge, teach the patient and family the importance of and rationale for oxygen therapy, safety precautions for oxygen use, how to use the oxygen delivery device, how to contact the supplier of medical equipment, and when to contact the health care provider.
- Discuss signs of oxygen toxicity that the patient must report to the health care provider, such as confusion, headache, decreased level of consciousness, somnolence, carbon dioxide narcosis, and respiratory arrest.
Documentation
- Record your respiratory assessment findings, including the following:
- Method of oxygen delivery
- Flow rate
- Patient’s response
- Adverse reactions or side effects
- Changes in the health care provider’s orders
- Report any unexpected outcome to the health care provider or nurse in charge.
Review Questions
1. When caring for a patient receiving oxygen by nasal cannula, which of the following is a priority to help maintain good skin integrity?
 Frequently applying moisturizing lotion to facial areas that come into contact with the cannula
Frequently applying moisturizing lotion to facial areas that come into contact with the cannula Removing the cannula every 2 hours for no longer than 10 minutes
Removing the cannula every 2 hours for no longer than 10 minutes Assessing the patient’s external ears, nares, and nasal mucosa for breakdown at least once per shift
Assessing the patient’s external ears, nares, and nasal mucosa for breakdown at least once per shift Instructing the patient to inform staff of any problems with facial dryness or cracking
Instructing the patient to inform staff of any problems with facial dryness or cracking
2. When caring for a patient who is receiving oxygen by simple face mask, which action ensures that the rate of oxygen being delivered is appropriate?
 Frequently asking the patient how he or she is breathing
Frequently asking the patient how he or she is breathing Ensuring that the oxygen tubing is pulled tight, with little or no slack
Ensuring that the oxygen tubing is pulled tight, with little or no slack Securing the oxygen tubing to the patient’s clothing to prevent tugging
Securing the oxygen tubing to the patient’s clothing to prevent tugging Assessing for proper placement of the mask on the patient’s face
Assessing for proper placement of the mask on the patient’s face
3. When caring for a patient for whom oxygen by nonrebreathing mask has been ordered, which action ensures appropriate oxygen delivery?
 Looping the oxygen tubing around the side rail of the bed
Looping the oxygen tubing around the side rail of the bed Assessing breath sounds every shift
Assessing breath sounds every shift  Securing the tubing snugly to the patient’s gown
Securing the tubing snugly to the patient’s gown  Assessing that the reservoir bag stays inflated
Assessing that the reservoir bag stays inflated
4. When caring for a patient who is receiving supplemental oxygen by face tent, which action ensures that the oxygen is flowing?
 Testing the closing capacity of the mask’s valves
Testing the closing capacity of the mask’s valves Routinely monitoring the seal over the patient’s mouth and nose
Routinely monitoring the seal over the patient’s mouth and nose Ensuring that a mist is always present
Ensuring that a mist is always present Regularly verifying that the mask is positioned loosely
Regularly verifying that the mask is positioned loosely
5. What would the nurse do when receiving an order to increase the delivery rate of a patient’s oxygen per nasal cannula from 1 L/min to 3 L/min?
 Encourage the patient to take deeper breaths in order to get more oxygen
Encourage the patient to take deeper breaths in order to get more oxygen Change the device from nasal cannula to simple face mask
Change the device from nasal cannula to simple face mask  Ensure that humidification is present
Ensure that humidification is present Adjust the float ball on the flow meter to 3 L/min.
Adjust the float ball on the flow meter to 3 L/min.
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.

