Respiratory Care and Suctioning
Select a Skill:
- » Ensuring Oxygen Safety
- » Setting Oxygen Flow Rates
- » Applying a Nasal Cannula or Face Mask
- » Maintaining an Airway
- » Providing Tracheostomy Care
- » Performing Oropharyngeal Suctioning
- » Performing Nasotracheal and Nasopharyngeal Suctioning
Take the Review Test:

Safety
- Using water-soluble lubricant helps avoid lipoid aspiration pneumonia. Excessive lubricant can occlude the catheter.
- Be sure to insert the catheter as the patient inhales, especially when inserting the catheter into the trachea. Inhalation opens the epiglottis.
- Do not insert the catheter during swallowing, or the catheter will probably enter the esophagus. Never apply suction during catheter insertion. The patient should cough. If the patient gags or becomes nauseated, the catheter is probably in the esophagus and must be removed.
- When using the nasal approach, perform tracheal suctioning before pharyngeal suctioning whenever possible. The mouth and pharynx contain more bacteria than the trachea.
- Monitor the patient’s vital signs and saturation of peripheral oxygen (SpO2) throughout the suction procedure. Stop suctioning if the patient’s pulse drops by more than 20 beats/min or increases by more than 40 beats/min, or if the pulse oximetry reading falls below 90%—or by more than 5% from the patient’s baseline.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
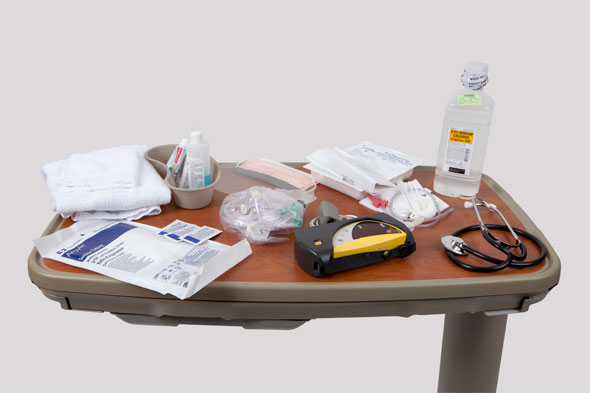
Pulse oximeter
Suction tubing
Suctioning Kit
- Catheter
- Sterile gloves
- Sterile drape
- Container for sterile saline or water
1 L bottle sterile normal saline
Emesis basin and Oral hygiene supplies
Face shield, mask, goggles (optional)
Stethoscope
Delegation
The skill of nasotracheal suctioning may not be delegated to NAP.
Preparation
- Assess for risk factors for upper or lower airway obstruction, including obstructive lung disease, pulmonary infection, impaired mobility, sedation, decreased consciousness, seizures, presence of a feeding tube, decreased gag or cough reflex, and impaired swallowing ability.
- Be alert for anxiety, lack of concentration, lethargy, fatigue, dizziness, irritability, pallor, dyspnea, and use of accessory muscles. Throughout the procedure, monitor vital signs (including peripheral blood oxygen saturation) and assess for signs of airway obstruction requiring suctioning, including wheezing, crackles, or gurgling; restlessness; ineffective coughing; absent or diminished breath sounds; tachypnea; hypertension or hypotension; cyanosis; decreased consciousness, especially acute; excessive nasal secretions, drooling, or gastric secretions; and vomitus in the mouth.
- Assess for anatomical factors that may influence airway function: recent surgery; head, chest, or neck tumors; facial or nasal trauma; and neuromuscular disease or factors that affect the volume and consistency of secretions, including fluid imbalance, inadequate humidity, infection, allergies, or sinus drainage.
- Evaluate a patient’s need for suctioning, and consider contraindications such as the following:
- Facial or neck trauma/surgery or gastric surgery
- Bleeding disorders or nasal bleeding
- Epiglottitis or croup
- Laryngospasm or irritable airway
- Explain and assess the patient’s understanding of the procedure. Advise the patient that temporary coughing, sneezing, gagging, or shortness of breath can be expected.
- Help the patient assume a position that is comfortable for both of you, such as the semi-Fowler’s position or sitting upright with the head hyperextended, unless contraindicated.
Follow-up
- Compare the patient’s vital signs, cardiopulmonary assessments, and SpO2 values before and after suctioning.
- Ask the patient if breathing is easier and congestion is decreased.
- Observe the character of airway secretions.
Documentation
- Record the amount, consistency, color, and odor of secretions, as well as the size of catheter, route of suctioning, and the patient’s response to suctioning.
- Document the patient’s presuctioning and postsuctioning vital signs, cardiopulmonary status, and ventilation measures.
Review Questions
1. Which action is part of the preparation for nasotracheal suctioning?
 Place the patient in a supine position.
Place the patient in a supine position. Preoxygenate the patient with 100% oxygen.
Preoxygenate the patient with 100% oxygen. Suction 100 mL of warm tap water to flush the suction catheter.
Suction 100 mL of warm tap water to flush the suction catheter. Place water-soluble lubricant onto the open sterile catheter package.
Place water-soluble lubricant onto the open sterile catheter package.
2. Which response would the nurse report immediately if it occurred in association with nasotracheal suctioning?
 Patient complains of discomfort during the procedure
Patient complains of discomfort during the procedure Patient has a severe bout of nonproductive coughing and complains of sore throat
Patient has a severe bout of nonproductive coughing and complains of sore throat  After oxygen delivery device has been reapplied on completion of the procedure, patient’s pulse oximetry reading falls to 88%
After oxygen delivery device has been reapplied on completion of the procedure, patient’s pulse oximetry reading falls to 88%  Patient’s pulse rate increases by 10 beats/min
Patient’s pulse rate increases by 10 beats/min
3. While suctioning the nasotracheal airway, the nurse notes that a patient’s pulse rate has fallen from 102 beats/min to 80 beats/min. What is the best course of action?
 Encourage the patient to take several deep breaths.
Encourage the patient to take several deep breaths. Interrupt suction to the catheter for at least 10 seconds.
Interrupt suction to the catheter for at least 10 seconds. Discontinue suctioning by removing the suction catheter.
Discontinue suctioning by removing the suction catheter. Assess the patient’s pulse oximetry reading to see if oxygenation is adequate.
Assess the patient’s pulse oximetry reading to see if oxygenation is adequate.
4. As a nasotracheal catheter is inserted to suction the airway, a patient begins to gag and says, “I feel like I’m going to throw up.” What is the nurse’s best response?
 Complete the catheter insertion in 5 seconds or less.
Complete the catheter insertion in 5 seconds or less. Remove the catheter.
Remove the catheter. Encourage the patient to take several deep breaths to minimize the nausea.
Encourage the patient to take several deep breaths to minimize the nausea. Stop advancing the catheter, and allow the patient to rest for several minutes.
Stop advancing the catheter, and allow the patient to rest for several minutes.
5. How does the nurse evaluate the effect of nasotracheal suctioning on a patient’s respiratory status?
 Asking the patient about symptoms of respiratory difficulty
Asking the patient about symptoms of respiratory difficulty  Comparing respiratory assessment data from before and after the suctioning procedure.
Comparing respiratory assessment data from before and after the suctioning procedure. Confirming that the patient’s pulse oximetry value is >90%
Confirming that the patient’s pulse oximetry value is >90% Auscultating the patient’s chest after suctioning
Auscultating the patient’s chest after suctioning
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.

