Wound and Pressure Ulcer Care
Select a Skill:
- » Assessing Wounds
- » Irrigating Wounds
- » Changing a Dressing
- » Using Wound Drainage Systems
- » Caring for Pressure Ulcers
Take the Review Test:
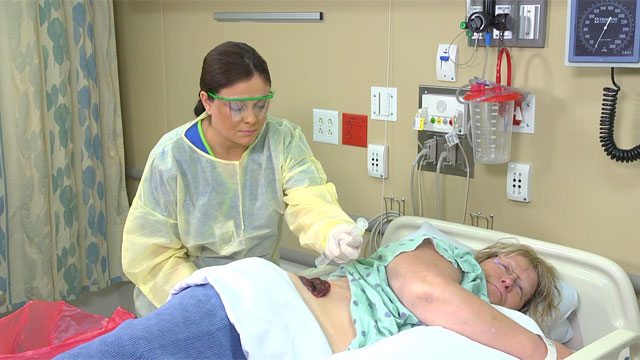
Safety
- Perform meticulous hand hygiene, and follow proper infection control procedures before and after removing soiled dressings. Wear clean gloves during wound care.
- Use sterile irrigation solution for postoperative wounds. Use clean solution for chronic wounds.
- Irrigate so that the solution flows from the least contaminated area (healthy tissue) toward the most contaminated area (infected tissue), and from the area being cleansed to a lower, distal area.
- Consider using a handheld shower technique for wound cleansing in an ambulatory patient, keeping the shower head about 12 inches from the wound.
- Never substitute a skin cleanser for a wound cleanser; they are not the same.
- Do not force a catheter into the wound. Place the syringe carefully to keep the pressure of the flowing solution from becoming too high.
- Consider culturing a wound if it has a foul odor, becomes inflamed, or begins to drain, or if the patient becomes febrile.
- If bleeding occurs, serosanguineous drainage appears, or the suture line on a surgical wound opens or extends, flush with less pressure during the next irrigation. Notify the health care provider of the bleeding.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
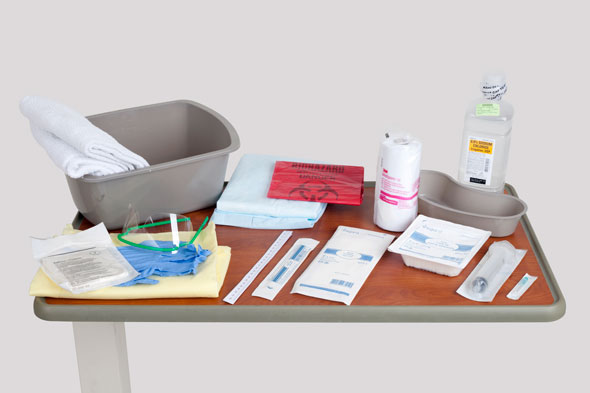
Irrigant/cleansing solution
Emesis basin
Sterile irrigation 30-mL syringe with sterile soft angiocatheter
Personal protective equipment:
- Clean gloves
- Sterile gloves
- Gown
- Goggles (if needed)
Waterproof pad
ABD dressing
Metapore tape
4x4 gauze
Disposable biohazard bag
Measuring gauge
Cotton tipped applicators
Basin
Towels
Delegation
The skill of sterile wound irrigation may not be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). You may, however, delegate the cleansing of chronic wounds using clean technique. It remains your responsibility as the nurse to assess and document the wound characteristics. Be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Instruct NAP to notify you when the wound is exposed, so that an assessment can be completed.
- Instruct NAP to report any patient complaints of wound pain.
Preparation
- Review the order to irrigate an open wound, and note the type of solution to be used.
- Review the most recently charted wound assessment for comparison.
- Determine if the patient has a history of allergies to any medication, antiseptic, latex, tape, or other dressing material.
- If needed, administer an analgesic 30 minutes to 45 minutes before wound irrigation.
- Educate the patient and family members about the procedure.
Follow-up
- Have the patient rate his or her level of pain on a scale of 0 to 10.
- Monitor the type of tissue in the wound bed.
- Inspect the dressing periodically, according to your agency’s policy.
- Evaluate the integrity of the skin surrounding the wound.
- Look for irrigant retained in the wound.
Documentation
- Record your wound assessment before and after irrigation, including the following:
- Amount, color, and odor of any drainage on the removed dressing
- Amount and type of solution used
- Irrigation device used
- Patient’s tolerance of the procedure
- Type of dressing applied after the irrigation
- Immediately report to the health care provider any evidence of fresh bleeding, sharp pain, or increased pain, as well as any irrigant retention, or signs of shock.
Review Questions
1. When irrigating a wound, how would the nurse know the right amount of pressure to apply?
 Calculate the wound size.
Calculate the wound size. Follow the general rule of keeping the pressure between 4 and 15 psi.
Follow the general rule of keeping the pressure between 4 and 15 psi. Keep the pressure strong enough to cause moderate pain.
Keep the pressure strong enough to cause moderate pain. Gentle enough that it does not create a splash off of the wound.
Gentle enough that it does not create a splash off of the wound.
2. Which action should the nurse avoid before irrigating a patient’s foot wound?
 Assess the patient for a history of allergies to tape and irrigating solution.
Assess the patient for a history of allergies to tape and irrigating solution. Review the provider’s orders for the type of irrigating solution to be used.
Review the provider’s orders for the type of irrigating solution to be used. Assess the patient’s pain on a scale of 0 to 10.
Assess the patient’s pain on a scale of 0 to 10. Warm the irrigant to body temperature in the microwave.
Warm the irrigant to body temperature in the microwave.
3. Which device is used for wound irrigation?
 19-gauge needle attached to a 10-mL syringe
19-gauge needle attached to a 10-mL syringe  19-gauge needle attached to a 35-mL syringe
19-gauge needle attached to a 35-mL syringe Sterile container held 30.5 cm (12 inches) above the wound
Sterile container held 30.5 cm (12 inches) above the wound Foley irrigating syringe
Foley irrigating syringe
4. Which imaging study or diagnostic test would the nurse review to determine if the pressure ulcer on a patient’s left heel is infected?
5. A nurse is irrigating a patient’s abdominal wound 2 days postoperatively. Which finding would need to be reported to the health care provider?
 Drainage that was not present previously
Drainage that was not present previously Redness at the abdominal suture line
Redness at the abdominal suture line Granulation tissue in the wound bed
Granulation tissue in the wound bed The patient reports less pain
The patient reports less pain
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.

